Oscillations
An neural oscillation is the rhythmic and/or repetitive electrical activity generated spontaneously and in response to stimuli by neural tissue in the central nervous system. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3811101/#:~:text=The term “brain (or%20neural,processes%20has%20become%20increasingly%20evident.
The following discusses some common neural oscillations.
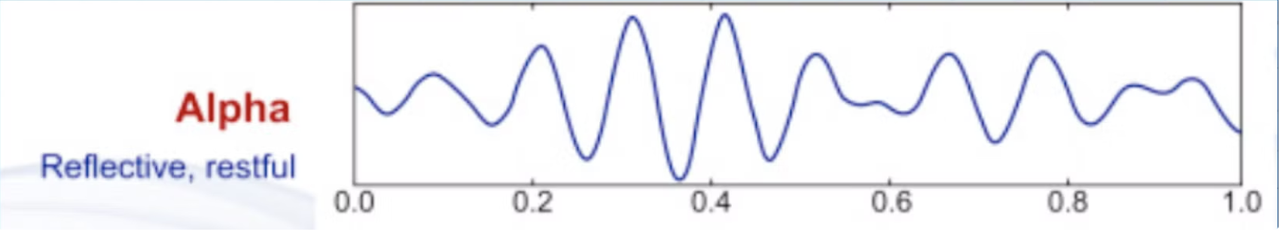
Alpha waves
Alpha waves are a type of brainwave associated with a relaxed yet alert state of consciousness. They typically have a frequency range of 8 to 13 Hertz (Hz) and are often observed when a person is awake but in a calm and unfocused state, such as during meditation or daydreaming. Alpha waves are characterized by regular, smooth oscillations and are commonly found in the posterior regions of the brain. Their presence can be an indicator of a relaxed mind.
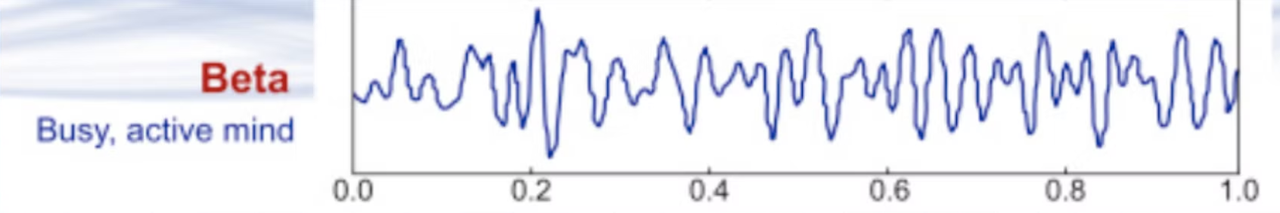
Beta waves
Beta waves are higher-frequency brain waves ranging from 13 to 30 Hz. These waves are associated with active, alert, and focused mental states. When you're awake, engaged in problem-solving, or concentrating on a task, your brain often generates beta waves. They are prevalent in the frontal and central regions of the brain and are linked to cognitive functions like attention, decision-making, and active thinking.
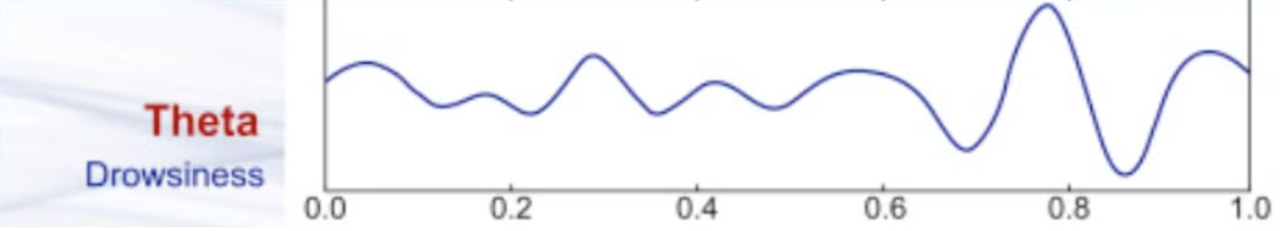
Theta waves
Theta waves have frequencies ranging from 4 to 7 Hz. They are commonly found during light sleep, meditation, and deep relaxation. Theta waves are also associated with creative thinking, intuition, and the early stages of memory formation. When you experience vivid dreams during REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, your brain often produces theta waves, contributing to the dream experience.
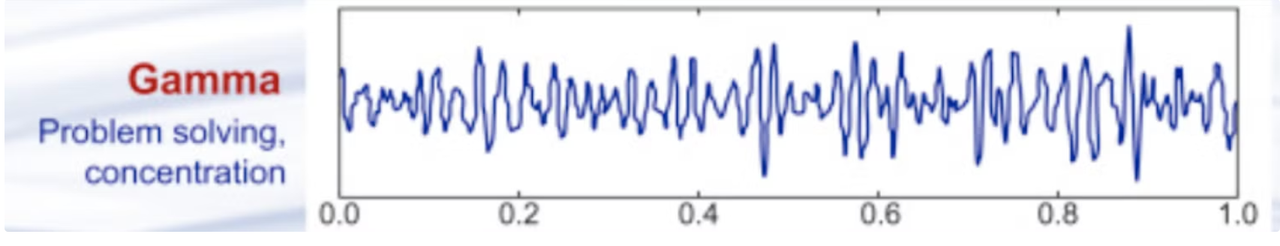
Gamma waves
Gamma waves are the fastest brainwaves, with frequencies exceeding 30 Hz. They are thought to play a role in complex cognitive processes, such as memory, perception, and consciousness. Gamma waves are often associated with the binding of sensory information and the integration of different brain regions' activities. Their presence is vital for forming coherent thoughts and experiences. Please note that it is currently impossible to record true gamma oscillations from scalp EEG; this is typically achieved through intracranial recordings.
Delta waves
Delta waves are slow brain waves with frequencies below 4 Hz.
They are predominantly observed during deep sleep stages, such as Sleep Stages 3 and 4.
Important note: While frequency bands are often labeled with specific ranges (e.g., alpha: 8-13 Hz), the function of oscillations in the same frequency range can differ depending on the brain region and the context in which they occur.
For example, Mu oscillations (8-13 Hz) over the motor cortex are related to motor functions, such as motor planning, execution, or the inhibition of movement. In contrast, alpha oscillations (8-13 Hz) over the visual cortex are associated with attention and sensory processing, often linked to the suppression of visual input when not actively engaged in a visual task.
This highlights that the same frequency band (e.g., 8-13 Hz) can reflect different processes depending on the brain area and context. So, while the frequency range is consistent, the meaning and function of those oscillations are not. Frequency bands don't necessarily always map strictly to specific neural processes; the spatial location and task demands are critical in determining their role.